#include <dict0mem.h>
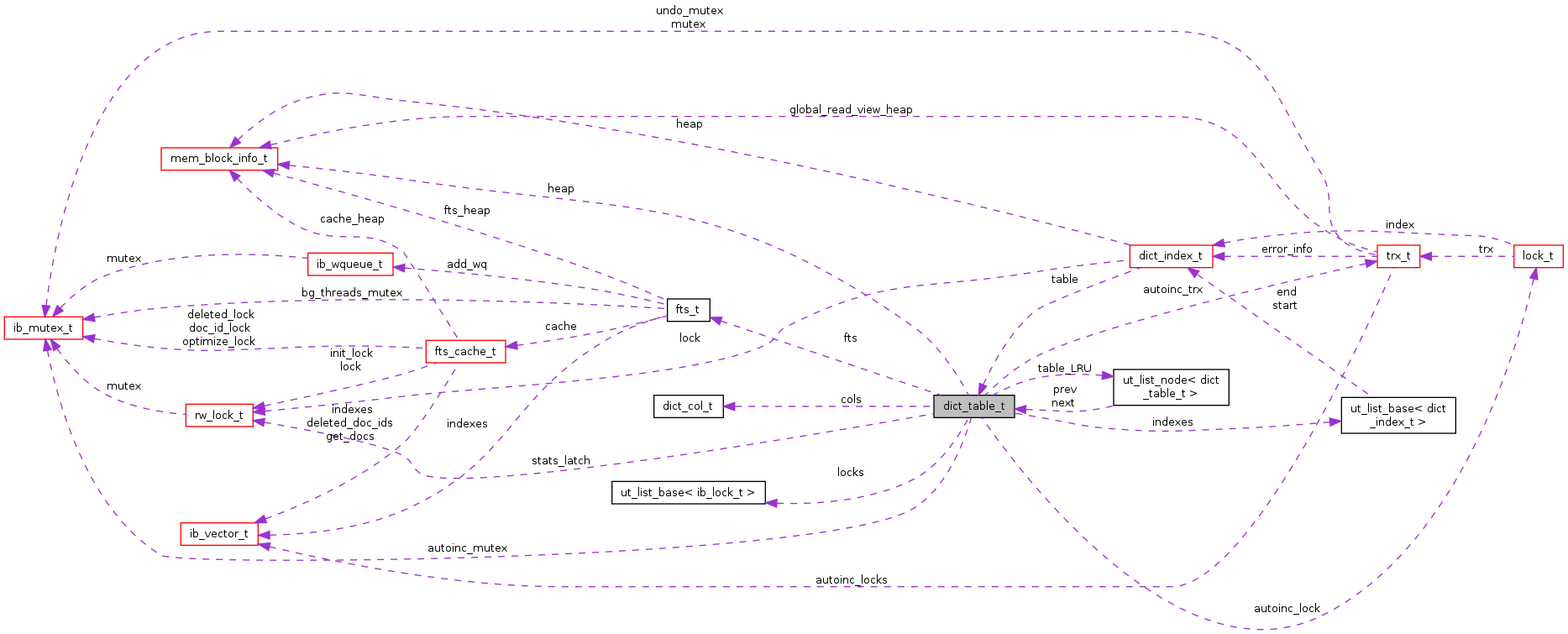
Detailed Description
Data structure for a database table. Most fields will be
initialized to 0, NULL or FALSE in dict_mem_table_create().
Field Documentation
| ib_uint64_t dict_table_t::autoinc |
autoinc counter value to give to the next inserted row
| lock_t* dict_table_t::autoinc_lock |
!< The following fields are used by the AUTOINC code. The actual collection of tables locked during AUTOINC read/write is kept in trx_t. In order to quickly determine whether a transaction has locked the AUTOINC lock we keep a pointer to the transaction here in the autoinc_trx variable. This is to avoid acquiring the lock_sys_t::mutex and scanning the vector in trx_t.
When an AUTOINC lock has to wait, the corresponding lock instance is created on the trx lock heap rather than use the pre-allocated instance in autoinc_lock below. a buffer for an AUTOINC lock for this table: we allocate the memory here so that individual transactions can get it and release it without a need to allocate space from the lock heap of the trx: otherwise the lock heap would grow rapidly if we do a large insert from a select
| ib_mutex_t* dict_table_t::autoinc_mutex |
mutex protecting the autoincrement counter
| volatile os_once::state_t dict_table_t::autoinc_mutex_created |
Creation state of autoinc_mutex member
| const trx_t* dict_table_t::autoinc_trx |
The transaction that currently holds the the AUTOINC lock on this table. Protected by lock_sys->mutex.
| unsigned dict_table_t::big_rows |
flag: TRUE if the maximum length of a single row exceeds BIG_ROW_SIZE; initialized in dict_table_add_to_cache()
| unsigned dict_table_t::cached |
TRUE if the table object has been added to the dictionary cache
| unsigned dict_table_t::can_be_evicted |
TRUE if it's not an InnoDB system table or a table that has no FK relationships
| const char* dict_table_t::col_names |
Column names packed in a character string "name1\0name2\0...nameN\0". Until the string contains n_cols, it will be allocated from a temporary heap. The final string will be allocated from table->heap.
| dict_col_t* dict_table_t::cols |
array of column descriptions
| unsigned dict_table_t::corrupted |
TRUE if table is corrupted
| char* dict_table_t::data_dir_path |
NULL or the directory path specified by DATA DIRECTORY
| trx_id_t dict_table_t::def_trx_id |
transaction id that last touched the table definition, either when loading the definition or CREATE TABLE, or ALTER TABLE (prepare, commit, and rollback phases)
| const char* dict_table_t::dir_path_of_temp_table |
NULL or the directory path where a TEMPORARY table that was explicitly created by a user should be placed if innodb_file_per_table is defined in my.cnf; in Unix this is usually /tmp/..., in Windows temp...
| ibool dict_table_t::does_not_fit_in_memory |
this field is used to specify in simulations tables which are so big that disk should be accessed: disk access is simulated by putting the thread to sleep for a while; NOTE that this flag is not stored to the data dictionary on disk, and the database will forget about value TRUE if it has to reload the table definition from disk
| unsigned dict_table_t::drop_aborted |
TRUE if some indexes should be dropped after ONLINE_INDEX_ABORTED or ONLINE_INDEX_ABORTED_DROPPED
| unsigned dict_table_t::fk_max_recusive_level |
maximum recursive level we support when loading tables chained together with FK constraints. If exceeds this level, we will stop loading child table into memory along with its parent table
| unsigned dict_table_t::flags |
DICT_TF_...
| unsigned dict_table_t::flags2 |
DICT_TF2_...
| dict_foreign_set dict_table_t::foreign_set |
set of foreign key constraints in the table; these refer to columns in other tables
| mem_heap_t* dict_table_t::heap |
memory heap
| unsigned dict_table_t::ibd_file_missing |
TRUE if this is in a single-table tablespace and the .ibd file is missing; then we must return in ha_innodb.cc an error if the user tries to query such an orphaned table
| table_id_t dict_table_t::id |
id of the table
| hash_node_t dict_table_t::id_hash |
hash chain node
| ut_list_base< dict_index_t > dict_table_t::indexes |
list of indexes of the table
| ut_list_base< ib_lock_t > dict_table_t::locks |
list of locks on the table; protected by lock_sys->mutex
| ulint dict_table_t::magic_n |
magic number
| lint dict_table_t::memcached_sync_count |
count of how many handles are opened to this table from memcached; DDL on the table is NOT allowed until this count goes to zero. If it's -1, means there's DDL on the table, DML from memcached will be blocked.
| unsigned dict_table_t::n_cols |
number of columns
| unsigned dict_table_t::n_def |
number of columns defined so far
| ulint dict_table_t::n_foreign_key_checks_running |
count of how many foreign key check operations are currently being performed on the table: we cannot drop the table while there are foreign key checks running on it!
| ulint dict_table_t::n_rec_locks |
Count of the number of record locks on this table. We use this to determine whether we can evict the table from the dictionary cache. It is protected by lock_sys->mutex.
| ulint dict_table_t::n_ref_count |
count of how many handles are opened to this table; dropping of the table is NOT allowed until this count gets to zero; MySQL does NOT itself check the number of open handles at drop
| ulong dict_table_t::n_waiting_or_granted_auto_inc_locks |
This counter is used to track the number of granted and pending autoinc locks on this table. This value is set after acquiring the lock_sys_t::mutex but we peek the contents to determine whether other transactions have acquired the AUTOINC lock or not. Of course only one transaction can be granted the lock but there can be multiple waiters.
| char* dict_table_t::name |
table name
| hash_node_t dict_table_t::name_hash |
hash chain node
| trx_id_t dict_table_t::query_cache_inv_trx_id |
transactions whose trx id is smaller than this number are not allowed to store to the MySQL query cache or retrieve from it; when a trx with undo logs commits, it sets this to the value of the trx id counter for the tables it had an IX lock on
| ib_quiesce_t dict_table_t::quiesce |
Quiescing states, protected by the dict_index_t::lock. ie. we can only change the state if we acquire all the latches (dict_index_t::lock) in X mode of this table's indexes.
| dict_foreign_set dict_table_t::referenced_set |
list of foreign key constraints which refer to this table
| unsigned dict_table_t::space |
space where the clustered index of the table is placed
| ulint dict_table_t::stat_clustered_index_size |
approximate clustered index size in database pages
| unsigned dict_table_t::stat_initialized |
TRUE if statistics have been calculated the first time after database startup or table creation
| ib_uint64_t dict_table_t::stat_modified_counter |
when a row is inserted, updated, or deleted, we add 1 to this number; we calculate new estimates for the stat_... values for the table and the indexes when about 1 / 16 of table has been modified; also when the estimate operation is called for MySQL SHOW TABLE STATUS; the counter is reset to zero at statistics calculation; this counter is not protected by any latch, because this is only used for heuristics
| ib_uint64_t dict_table_t::stat_n_rows |
approximate number of rows in the table; we periodically calculate new estimates
| ib_uint32_t dict_table_t::stat_persistent |
The two bits below are set in the ::stat_persistent member and have the following meaning:
- _ON=0, _OFF=0, no explicit persistent stats setting for this table, the value of the global srv_stats_persistent is used to determine whether the table has persistent stats enabled or not
- _ON=0, _OFF=1, persistent stats are explicitly disabled for this table, regardless of the value of the global srv_stats_persistent
- _ON=1, _OFF=0, persistent stats are explicitly enabled for this table, regardless of the value of the global srv_stats_persistent
- _ON=1, _OFF=1, not allowed, we assert if this ever happens.
| ulint dict_table_t::stat_sum_of_other_index_sizes |
other indexes in database pages
| ib_uint32_t dict_table_t::stats_auto_recalc |
The two bits below are set in the ::stats_auto_recalc member and have the following meaning:
- _ON=0, _OFF=0, no explicit auto recalc setting for this table, the value of the global srv_stats_persistent_auto_recalc is used to determine whether the table has auto recalc enabled or not
- _ON=0, _OFF=1, auto recalc is explicitly disabled for this table, regardless of the value of the global srv_stats_persistent_auto_recalc
- _ON=1, _OFF=0, auto recalc is explicitly enabled for this table, regardless of the value of the global srv_stats_persistent_auto_recalc
- _ON=1, _OFF=1, not allowed, we assert if this ever happens.
| byte dict_table_t::stats_bg_flag |
see BG_STAT_* above. Writes are covered by dict_sys->mutex. Dirty reads are possible.
| ib_time_t dict_table_t::stats_last_recalc |
Timestamp of last recalc of the stats
| rw_lock_t* dict_table_t::stats_latch |
this latch protects: dict_table_t::stat_initialized dict_table_t::stat_n_rows (*) dict_table_t::stat_clustered_index_size dict_table_t::stat_sum_of_other_index_sizes dict_table_t::stat_modified_counter (*) dict_table_t::indexes*::stat_n_diff_key_vals[] dict_table_t::indexes*::stat_index_size dict_table_t::indexes*::stat_n_leaf_pages (*) those are not always protected for performance reasons
| volatile os_once::state_t dict_table_t::stats_latch_created |
Statistics for query optimization Creation state of 'stats_latch'.
| ulint dict_table_t::stats_sample_pages |
the number of pages to sample for this table during persistent stats estimation; if this is 0, then the value of the global srv_stats_persistent_sample_pages will be used instead.
| ut_list_node< dict_table_t > dict_table_t::table_LRU |
node of the LRU list of tables
| unsigned dict_table_t::to_be_dropped |
TRUE if the table is to be dropped, but not yet actually dropped (could in the bk drop list); It is turned on at the beginning of row_drop_table_for_mysql() and turned off just before we start to update system tables for the drop. It is protected by dict_operation_lock
The documentation for this struct was generated from the following file:
- include/dict0mem.h
 1.8.1.2
1.8.1.2